NS1’s global traffic management load balancing (GTM-LB) solution is a Cloud-based solution designed to enable IT professionals to easily manage their global traffic across their private and public datacenters. This unique offering allows enterprises to leverage the NS1 platform’s authoritative DNS and advanced traffic routing capabilities for global traffic and seamlessly integrates with local load balancing solutions including Citrix, F5, HA Proxy, Kemp, and Nginx. This eliminates the need for enterprises to manage their own authoritative DNS, reduces costs and eliminates the need to maintain yet another on premises appliance.
This article takes a deep dive into NS1’s Shed Load (or load shedding) capabilities, one the components of NS1’s overall GTM-LB solution, and discusses how to use Shed Load to handle load balancing across your network.
What is Shed Load?
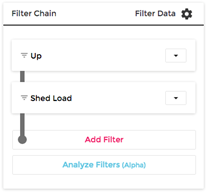
NS1’s Filter Chain technology leverages a series of filters that enable you to define how you want your authoritative DNS to handle traffic based upon specific situations. Shed Load is the name of the filter that shifts incoming traffic from one endpoint or datacenter to another based on a metric that you choose, such as specific connection limits or traffic limits for a specific datacenter. As the traffic increases toward that limit, you can shift the incoming traffic to another datacenter or cloud provider, ensuring you stay within your provisioned limits.
How Shed Load works
Shed Load uses a real-time data feed from your datacenter or endpoint to determine the current usage. It then measures the current usage against specific levels that you set. When traffic approaches an indicated level, Shed Load automatically begins sending traffic to the identified secondary datacenter. As traffic is reduced at the original datacenter, Shed Load automatically changes the traffic pattern again to return traffic to the original datacenter.
An example of how Shed Load works
This NS1 Managed DNS example is setup with monitors and Shed Load is setup to watch the active connections on datacenter1 and datacenter2. When the active connections on datacenter1 approach one of the predetermined levels, called watermarks in the Shed Load user interface, traffic will shift to datacenter2. In this graphic, datacenter1 shows 15 connections with a high watermark of 20. This means that datacenter2 will be handling some traffic for datacenter1.
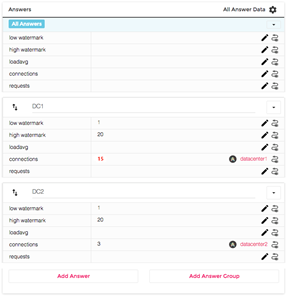
Figure 2 DNS Answers in the Filter Chain with Shed Load.
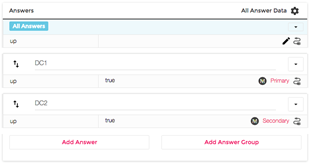
Figure 3 Filter Chain showing both monitored datacenters as 'up'.
How does the communication happen?
The API for Managed DNS is the communication portal between your datacenters and the Shed Load engine. The API is also used for the data feeds that allow Shed Load to monitor the real-time activities at your data centers and adjust the traffic when situations require it. Here is a curl example of information from datacenter1, showing the connections at 15.
curl -X POST -H "X-NSONE-Key: <key>" -d '{"datacenter1":{"connections":15}}' https://api.nsone.net/v1/feed/6f17c64300891c6fdfd05e3b88516dd4
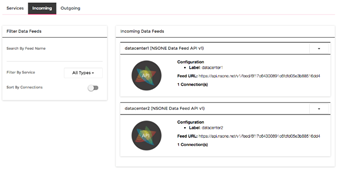
Figure 4 Setting up the data feed.
NS1 has the ability to help manage your global traffic management with advanced features such as load balancing DNS traffic across datacenters or endpoints.
For more information on setting up Load Shedding your NS1’s Managed DNS, please see the Knowledge Base and Solutions pages.